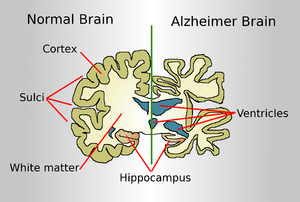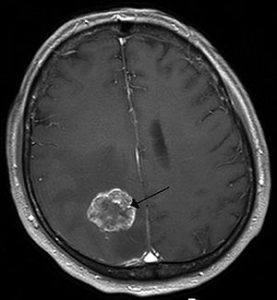
Meningioma is a brain tumor that is not metastatic and occurs even after a patient undergoes surgery and radiation. In such a situation, the patient with brain tumor is left with no treatment option.
Such aggressive tumors cannot be treated with drugs. These tumors occur in about 20% of the cases, making patients disabled or even prone to death.
Currently, researchers at the Northwestern University of Medicine have collaborated with the University of California and the University of Hong Kong.
They are on a mission to develop a novel drug that can inhibits the development of meningiomas. They are the most aggressive form of brain tumors. They are also working on identifying how accurately the drug are effective in destroying meningiomas.
These scientists have developed a new drug named abemaciclib, which is an anti-cancer agent. The drug was tested successful in a human clinical trial of selected patients. It was also tested on animal model of mouse.
Moreover, a three-dimensional brain tumor was extracted from living tissues. Such a tumor was known as organoids, and the drug was tested on this organoid and other cell cultures.
Investigators created two subgroups of meningiomas as their clinical outcome and recurrence rates were different. This new method of classifying tumors was more effective in predicting the recurrence rate as compared to the existing method.
Currently, patients with brain tumor have to undergo surgery. After undergoing surgery, a specimen of the tumor is examined by the doctor under a microscope and graded according to its aggression: one, two, or three.
But gradation of tumors has only 70% accuracy level. This implies that some tumors would behave in a way that does not resemble the specimen observed under the microscope.
In this study, we identified the patient who were suitable for being treated with abemaciclib, the novel anti-cancer drug. It is highly likely that the brain tumor of these patients would respond to this drug.
According to the lead investigator of this study, the drug has the potential to give such patients a longer life that is devoid of any symptoms. Dr. Stephen Magill is the corresponding author of this study and practices neurological surgery at the Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine. This study was published in the esteemed journal Nature Genetics.