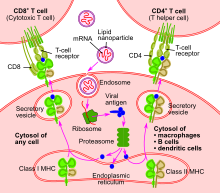
In clinical practice, healthcare workers may develop symptomatic COVID-19, so they are advised to take mRNA COVID vaccines as a recent study of researchers have found them to be very effective in preventing COVID-19. The study was published in the prestigious New England Journal of Medicine. In this study, the chances of developing symptoms of COVID-19 decreased as much as 89% in healthcare workers who received two doses of Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine. The Moderna vaccine was even more effective as it reduced the risk of developing COVID-19 by as much as 96%.
The researchers found that the vaccines were effective even in people above 50 years of age. Moreover, certain ethnic groups or racial groups who were more prone to developing COVID-19 were the ones who benefitted the most from vaccination drives. Healthcare workers who were exposed to COVID-19 patients also got immunity with vaccine. Finally, patients with underlying medical conditions benefitted from vaccines but the efficacy of the vaccine was lower in patients with compromised immunity.
The study was conducted by researchers working at the Carver College of Medicine, which is affiliated to the University of Iowa in the US. In this study, 5000 healthcare workers were evaluated: 1482 healthcare workers were found to be COVID-19 positive because they were having symptomatic illness. Moreover, 3449 healthcare workers had symptoms of COVID-19 but they were tested as negative. As many as 33 academic medical centers from the US participated in this study. The participants had to complete a survey questionnaire and provide information about their demographics, type of job, risk factors, severe disease associated with COVID-19, and the status of their vaccination.
Although all the subjects received two doses of mRNA vaccines, the risk of developing COVID-19 was reduced by 95% in Afro American subjects. On the other hand, the risk of COVID-19 declined by about 89% in Asian and Hispanic subjects and by about 94% in American Indian people. In subjects whose immunity was compromised with underlying disease, the risk of developing COVID-19 decreased by only 39%, regardless of whether they received a single dose or two doses of mRNA vaccine. Among pregnant women who received mRNA vaccine, the risk of developing COVID-19 decreased by about 77%. Even a single dose of the vaccine was quite effective in reducing the risk of COVID-19 as compared to those unvaccinated people. The study was conducted from December 2020 to May 2021.
